In recent years, almond milk has surged in popularity as a dairy alternative, touted for its health benefits and environmental friendliness. However, the truth behind the production of shelf almond milk reveals a more complex environmental impact than many realize. Let's delve into the environmental footprint of shelf almond milk production, explore the benefits of making it at home, and back it up with scientific data.
The Environmental Toll of Shelf Almond Milk Production
At first glance, almond milk seems like a sustainable choice. After all, almonds require less water to produce than dairy milk, and almond trees can thrive in semi-arid climates. However, the reality is more nuanced.
- Water Usage: While almond trees themselves are relatively water-efficient, the process of turning almonds into milk is water-intensive. According to research published in the journal *Science*, it takes approximately 130 pints of water to produce a single 8-ounce glass of almond milk.
- Land Use: Almond orchards require vast expanses of land, particularly in California where the majority of the world's almonds are grown. This can lead to habitat destruction, soil degradation, and loss of biodiversity.
- Pesticide Use: Almond production relies heavily on pesticides, which can have detrimental effects on local ecosystems and pollinators like bees.
- Packaging and Transport : Shelf almond milk typically comes in cartons or plastic bottles, contributing to the plastic waste problem. Additionally, the transportation of almond milk from production facilities to stores adds to its carbon footprint.
The Case for Homemade Almond Milk
Making almond milk at home offers several environmental benefits that counteract the drawbacks of shelf almond milk production:
- Reduced Packaging Waste : When you make almond milk at home, you can use reusable containers instead of single-use cartons or bottles, significantly reducing your plastic waste.
- Lower Carbon Footprint: By eliminating the need for processing and transportation, homemade almond milk has a smaller carbon footprint compared to its shelf-stable counterpart. Research from the University of California, Davis, highlights the water-saving benefits of homemade almond milk. By making almond milk at home, individuals can reduce their water footprint and contribute to water conservation efforts.
- Control Over Ingredients : Homemade almond milk allows you to control the quality of ingredients, ensuring that no unnecessary additives or preservatives are included.
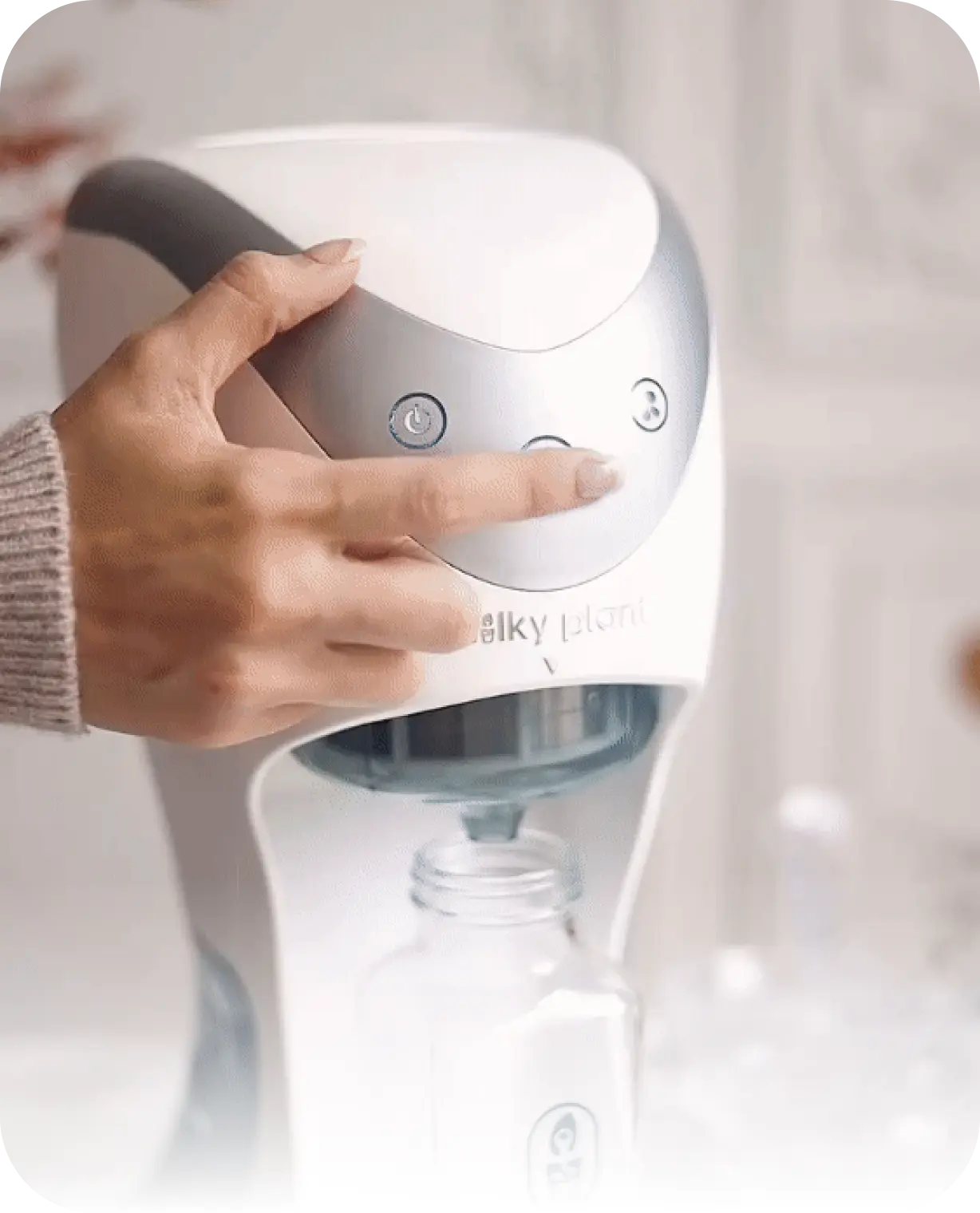
While almond milk has gained popularity as a dairy alternative, its environmental impact should not be overlooked. The production of shelf almond milk comes with significant water usage, land use, and packaging waste. However, making almond milk at home offers a greener alternative, with reduced carbon and water footprints, less packaging waste, and greater control over ingredients. We suggest trying to make your own almond milk at home with Milky Plant, an easy and healthy way to have your non-dairy milk ready in just 3 minutes, mess-free.
By incorporating scientific data into our understanding of almond milk production, we can make informed choices that align with our environmental values. Whether you're a dedicated environmentalist or simply looking to reduce your ecological footprint, homemade almond milk presents a sustainable and delicious option for your dairy-free needs.